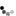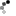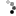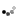 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...All prices are in All prices are in GBP
Categories
- Home
- Antique Prints
- Botany, Antique Print, Fern, oblong, rusty, Lindman
- Home
- Antique Prints
- Botanicals Antique Prints
- Botany, Antique Print, Fern, oblong, rusty, Lindman
- Home
- Antique Prints
- Botanicals Antique Prints
- Ferns/Foliage
- Botany, Antique Print, Fern, oblong, rusty, Lindman
Product Description
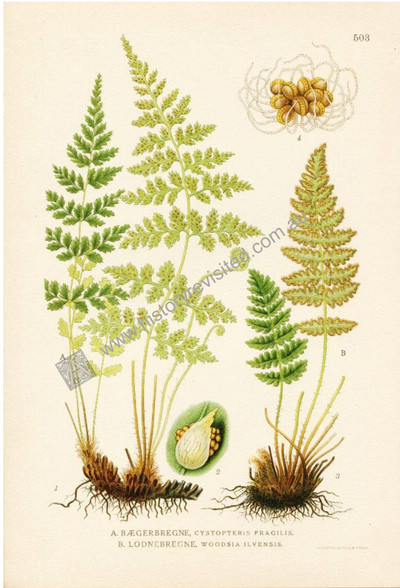
Botany, Antique Print, Chromolithograph, Cryopteris fragilis, Common fragile fern, Woodsia ilvensis, Rusty cliff fern, Lindman
Antique colored lithograph (chromolithograph) after Swedish botanist and botanial artist Carl Axel Magnus Lindman (1856-1928) for his folio "Bilder ur nordens Flora" (Pictures of Northern Flora). He was inspired by military botanical artist Johan Wilhelm Palmstuch who embarked on a scientific project to produce a series of impressive copper engravings, 1802–1819."Svensk Botanik" (Swedish Botany) was the first of its kind in Sweden.
Two fern structures are illustrated here, a bipinnate pinnatifid on the left showing the front and rear of the leaf, with two fiddleheads, rhizome, and detail of the protected spore housing complete with a protective scale. to the right the Woodsia illustrates a pinnate-pinnatfid. structure with a front view accompanied by a larger rear view showing the leaves edged by sori (spores). both emerge from a clumped rhisome, with a detail of sprouting spores above.
Published Stockholm by Wahlstrom & Widstrand, 1901-1905.
Condition = Excellent (no discoloration/tears)
Page size = 16.5 x 24.2 cm (6 1/2 x 9 1/2 inch)
Cytopteris fragilis (Bristle bladder-fern or Common fragile fern)
This fern is found world wide in shady, moist areas. The leaves are up to 30 or 40 centimeters long and on fleshy petioles or stems. Each leaf is divided into many pairs of leaflets, each of which is subdivided into lobed segments. This is termed a bipinnate pinnatifid. The underside of the leaf has many rounded sori containing the sporangia or spores. They are protected during development by a scale or film of tissue called the indusium which forms an umbrella-like cover.
Woodsia ilvensis (Oblong woodsia, Rusty woodsia or Rusty cliff fern)
This Woodsia ilvensis is commonly found on sunny exposed cliffs and rocky slopes of thin dry acidic soils. It is commonly in Scandanavia, eastern US, Japan, Alaska, coastal Greenland and the European Alps. it is an example of pinnate-pinnatifid leaf structure The Woodsia was first identified as a separate species in Bolton’s 1785 “Filices Brittanica”. The Woodsia ilvensis genus was established by Robert Brown in 1810 who named it after English botanist Joseph Woods, a fellow member of the Linnaen Society. Brown (1773-1858) made numerous contributions to plant taxonomy, especially Australian plant genera and species given his experience as botanist on Matthew Flinders circumnavigation of Australia 1800-1804. It is Brown that pointed out the “Lofty Mount” that was subsequently named Mount Lofty in the Adelaide Hills, South Australia. Mount Brown in the Flinders Ranges was named after him by Matthew Flinders on 9 March 1802.
Product Videos
-
 2 Bracken Fern...New River State Park Wagonr Access Fern Nature Trail 2 miles.
2 Bracken Fern...New River State Park Wagonr Access Fern Nature Trail 2 miles.